Real Help: A Peer-to-Peer Crypto Donation System
Real Help
give@real.help
https://real.help
Abstract.
Real Help is a blockchain donation platform based on x402 protocol, dedicated to complete transparency and direct impact. People share their verified true stories and needs. Donors choose the cases they want to support. And send funds directly via peer-to-peer crypto transfers. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, visible and verifiable to anyone, anytime. Real Help never touch your money. No fee, No commission, and No delay.
The total supply of HELP tokens is one billion. Of this amount, 500 million tokens constitute the initial liquidity supply, while the remaining 500 million tokens are minted publicly and fairly worldwide based on x402 protocol. 50% of the revenue from HELP tokens on-chain transaction fee will be donated to well-known charities. The remaining 50% of the revenue will be used to reward donors who contribute to projects on Real Help platform.
By combining blockchain transparency with a rewarding system, we create a sustainable economy where donors and recipients thrive together. Real Help, Real Hope !
Category.
- Chapter 1: Social Background of REAL HELP
- Chapter 2: The Nature and Establishment of Trust
- Chapter 3: What is Blockchain?
- Chapter 4: Why Can Blockchain Solve Trust Problems?
- Chapter 5: What is Real Help?
- Chapter 6: Help Tokenomics
- Chapter 7: Real Help Brand Strategy
Chapter 1: Social Background of Real Help
1.1 Global Crowdfunding Status and Difficulties
With the widespread adoption of the internet, social crowdfunding platforms have rapidly emerged, providing a “survival channel” for a large number of people in need. However, as the number of users grows, problems with traditional crowdfunding platforms have gradually become apparent:
- The platform’s information review mechanism is opaque, resulting in cases of false requests for help;
- The flow of funds is not traceable, forcing users to rely solely on the platform;
- Platform commissions and operating expenses are not transparent, with some platforms consistently charging high fee as operating costs;
- There is a lack of feedback and incentives for donations, and user contributions cannot be recorded or monetized.
These issues are continuously eroding users’ trust in crowdfunding, challenging the sustainability of donations.
1.2 A Broken Social Trust System
The trust mechanism in traditional crowdfunding is platform-central, requiring users to trust the centralized platform to review information, manage donations, and use them appropriately.
However:
- Platforms are not neutral: they themselves are sometimes profit-driven;
- Centralized power is not subject to community checks and balances: the platform essentially has the final say on whether cases are approved and how funds are allocated;
- Governance transparency is extremely low: users and the community lack channels for communication and decision-making, and there is no effective feedback for questions and suggestions.
Ultimately, crowdfunding has become a passive, low-feedback, low-trust, one-way process. Goodwill is gradually eroding, and the platform faces a “trust crisis.”
Chapter 2: The Nature and Establishment of Trust
Is there a method or technology that can solve the trust problem that has long plagued society? Before answering this question, we must first understand what trust is and how it is built.
2.1 What is “Trust”?
Trust is the psychological decision, based on judgment, to trust that others will fulfill their promises, refrain from actions that harm one’s own interests, and voluntarily cede some control under uncertainty and risk.
2.2 How is Trust Built?
Trust doesn’t just happen; it’s typically built gradually through the following mechanisms:
- Experience (repeated interactions)
- Positive past experiences (“you do what you say”);
- Each successful collaboration deepens trust, similar to the gradual accumulation of “reputation points.”
- Relationship Bonds (Emotional Identification)
- A sense of belonging to family, friends, and organizations;
- Built on emotional connections and shared values.
- Rules and Institutions (External Guarantees)
- Contracts, laws, and third-party endorsements;
- Trust is based on the assumption that violating trust has a cost.
- Verifiability (Information Transparency)
- I trust you because I can see what you’re doing.
Thus, the essence of trust is a subjective feeling and expected judgment. If the object of trust is changeable and modifiable, then trust will be affected.
Back to the original question: Is there a method or technology that can solve the trust problem that has long plagued society? In other words, can the mechanism of trust be transformed from subjective feelings and judgments to objective, immutable data? After all, people generally trust what they see more than what they hear (hearing is false, seeing is true). The answer is yes. Blockchain technology can, to a certain extent, solve this trust problem.
Chapter 3: What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof distributed ledger technology.
It is essentially a chain of data “blocks” linked in chronological order, with each block recording information about transactions or events over a specific period of time.
|
Features |
Brief Explanation |
|
Decentralized |
There is no single controller; the ledger is maintained by all nodes in the network. |
|
Immutable |
Once written, data cannot be altered; each block is linked to the hash of the previous block. |
|
Traceable |
All transactions can be traced back to their source. |
|
Open & Transparent |
Data is open to everyone and can be verified on-chain. |
|
Consensus |
Nodes reach consensus through algorithmic rules (such as PoW and PoS). |
Chapter 4: Why Can Blockchain Solve Trust Problems?
4.1 The traditional trust model relies on third-party intermediaries or authoritative institutions: governments, banks, notaries, e-commerce platforms, public authority systems, etc. The problem is: these institutions rely on human intervention, which can lead to errors, hacking, and even malicious behavior. They are also costly, inefficient, and subject to censorship and bias.
4.2 Solution: Blockchain replaces “institutional trust” with objective mechanism trust. Ultimately, the trust mechanism will be transferred from “people” to “code”, forming a system of “trusting code, not trusting people”.
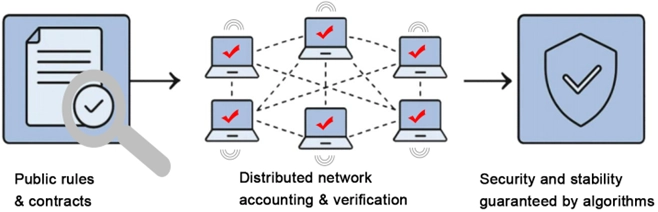
Through decentralization, consensus mechanisms, and immutability, blockchain creates a new trust model that enables cooperation and consensus even among participants who don’t trust each other. Trust isn’t based on trust in people (or organizations), but on the ability to verify that the rules remain unchanged and unmanipulated.
In the past, we passively trusted the platform; Now and in the future, we should proactively trust the mechanism.
Chapter 5: What is Real Help?
5.1 About REAL HELP
REAL HELP leverages blockchain technology to address the trust gaps found in traditional centralized platforms, establishing a new trust mechanism that rewards and empowers donations. The REAL HELP platform’s smart contracts run on the Ethereum and incorporate x402 protocal. Ultimately, the platform aims to develop into a system with its own regenerative economy.
5.2 Our Mission
To build a culture of help that rewards and empowers those who help – projects, society, and the world.
5.3 Fee & Charge
Real Help never touch users’ money, every transaction is peer to peer cryptocurrency transfer, without middlemen, without any charge. NO fee, NO commission, NO delay.
5.4 Automation
Real Help platform run on blockchain smart contract and will incorporate AI agent & x402 protocal to insure complete transparency of platform rules and data, and maximize automated execution.
Chapter 6: Help Tokenomics
Real Help issue the mint token “HELP” on the base chain, design a tokenomics model both donation to well-known charities and reward donors on REAL HELP platform.
Token Name: HELP
Deployment Chain: BASE
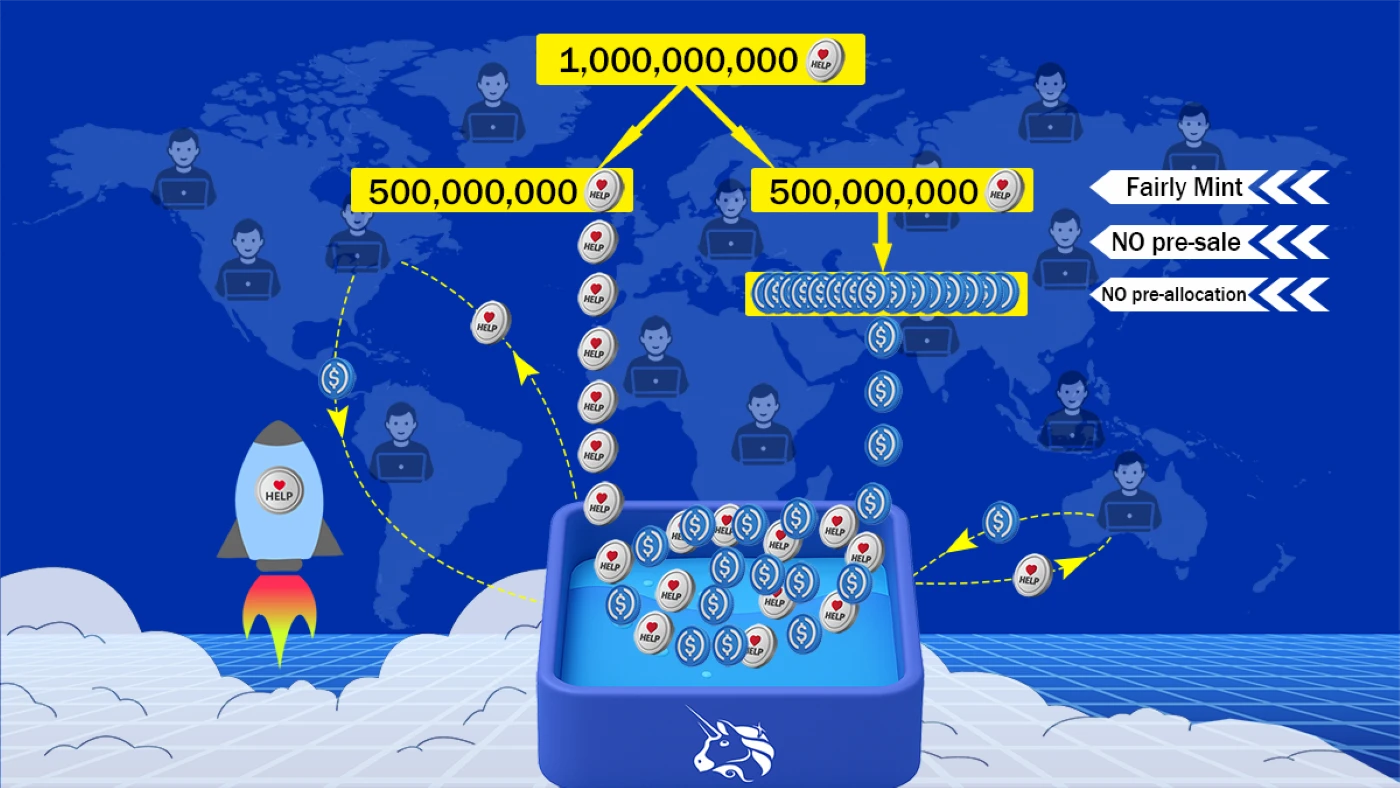
Total Supply: One billion(1,000,000,000)
Tokenomics:
The total supply of HELP tokens is one billion. Of this amount, 500 million tokens constitute the initial liquidity supply, while the remaining 500 million tokens are minted publicly and fairly worldwide. Throughout the entire HELP token minting process, there is no pre-sale, no pre-allocation, and Real Help platform does not hold any HELP tokens.
The total USDC raised from minting these 500 million HELP tokens serve as the initial liquidity capital, which, together with the initial liquidity supply 500 million HELP tokens, are both injected into the uniswap liquidity pool to establish the trading and exchange mechanism.

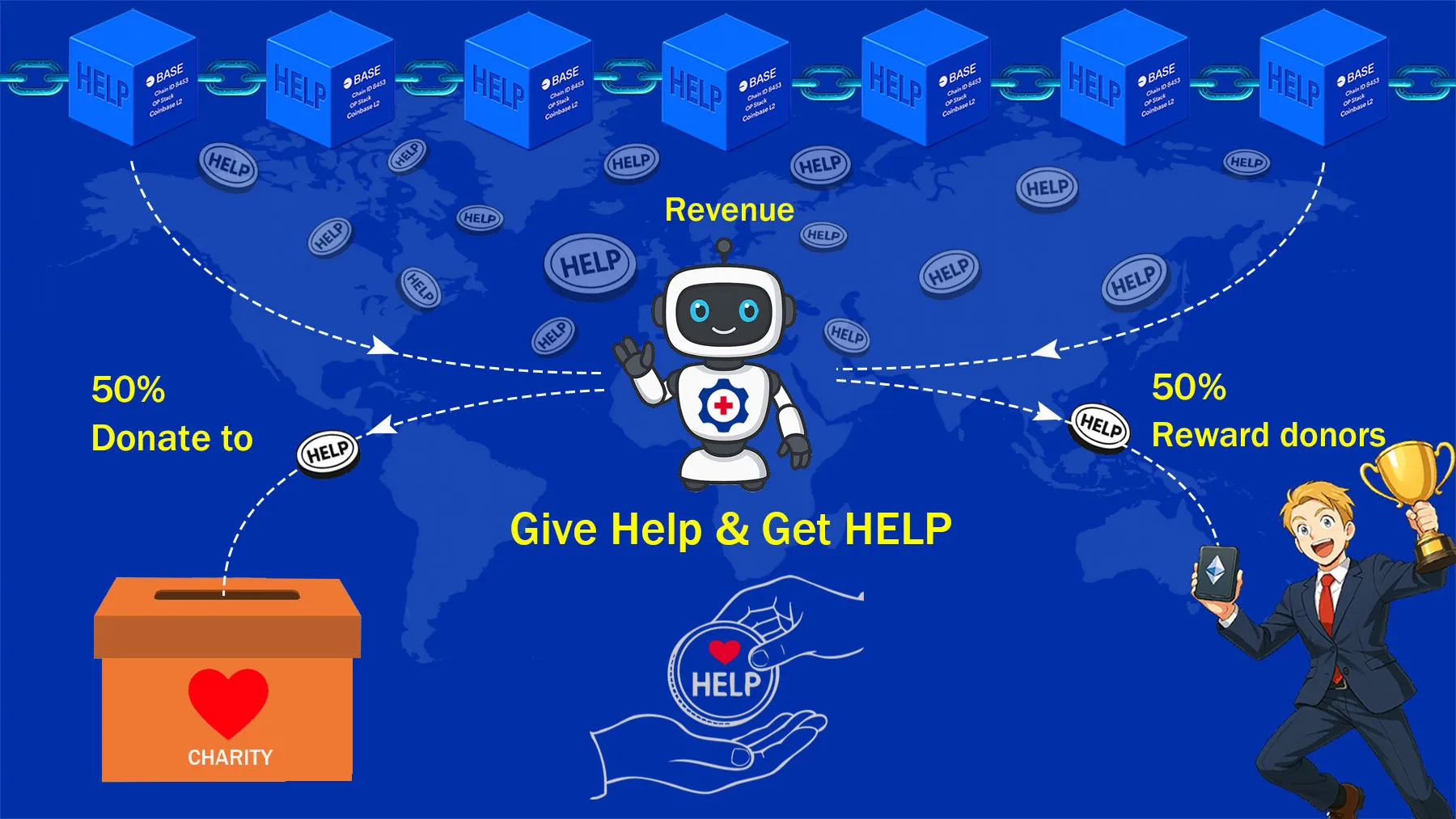
Give Help & Get HELP
50% of the revenue from HELP tokens on-chain transaction fee will be donated to well-known charities. The remaining 50% of the revenue will be used to reward donors who contribute to projects on Real Help platform.
By combining blockchain transparency with a rewarding system, we create a sustainable economy where donors and recipients thrive together.
Chapter 7: Real Help Brand Strategy
7.1 Redefine help culture
As a pioneer of worldwide blockchain and artificial intelligence-based donation platform, REAL HELP utilizes cutting-edge blockchain and AI technology based on the x402 protocol to combine a fully transparent donation with reward mechanism, creating a brand new token economy model of helping others and benefiting yourselves.
7.2 Brand Positioning
Positioning: The world’s leading blockchain donation platform.
Brand Keywords: Blockchain, Trust, Transparency, Donation, Charity.
Brand Slogan: Real Help, Real Hope!
7.3 Visual Identity

GIVE HELP & GET HELP
Donors who contribute to projects will be rewarded with HELP tokens.
More donations, more rewards.
